Abstract
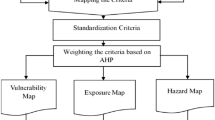
The present study attempts to delineate and map the groundwater potential zones (GWPZ) of the Barakar river basin in Jharkhand, through the integration of satellite images and geospatial techniques, using an analytical hierarchical process (AHP). Thematic layers of ten influential factors namely geomorphology, slope, curvature, drainage density, lineament density, geology, land use/land cover, rainfall, soil, and topographic wetness index are prepared and used for groundwater potentiality mapping. The analytical hierarchical process (AHP) method is adopted to assign weight to each of the ten criteria and their sub-criteria according to their role as an influential factor of groundwater recharge. The final groundwater potential map is produced by combining all ten thematic layers, using the weighted overlay analysis technique and spatial analysis tool in ArcGIS. The result shows that very poor, poor, moderate, good, and excellent groundwater potential zones covering an area of 284.95 km2 (4.42%), 1709.93km2 (26.56%), 1906.01 km2 (29.6%), 1244.20 km2 (19.32%), and 1292.52 km2 (20.07%) respectively. Good to excellent groundwater potential zone occupied an area of about 2536.72 km2 with flat topography and well-drained sandy soil characteristics in the downstream areas of the basin. South and western parts of the area presented poor to very poor groundwater prospect covering about 1994.88 km2 area with hard rock formation, steepest slope, and high altitude and drainage density. The obtained result is validated by considering the seasonal fluctuation of groundwater data where the value of R2 (0.70) and RMSE (7.633) indicated that obtained result is reliable and may help to a planner for sustainable management of groundwater resources.















Similar content being viewed by others
Abbreviations
- AHP :
-
Analytical hierarchy process
- CI :
-
Consistency index
- DEM :
-
Digital elevation model
- GIS :
-
Geographical information system
- LU/LC :
-
Land use/land cover
- MCDM :
-
Multicriteria decision-making
- SOI :
-
Survey of India
- MSL :
-
Mean sea level
- RMSE :
-
Root mean square error
- TFN :
-
Triangular fuzzy number
- SRTM :
-
Shuttle Radar Topography Mission
References
Acharyya SK, Shah BA (2007) Groundwater arsenic contamination affecting different geologic domains in India—a review: influence of geological setting, fluvial geomorphology and Quaternary stratigraphy. J Environ Sci Heal A 42(12):1795–1805
Aggarwal M, Saravanan S, Jacinth Jennifer J, Abijith D (2019) Delineation of groundwater potential zones for hard rock region in Karnataka using AHP and GIS. In: HM El-Askary, S Lee, E Heggy, B Pradhan (eds) Advances in Remote Sensing and Geo Informatics Applications. Springer International Publishing, pp 315–317. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-030-01440-7_71
Ahmed JB II, Mansor S (2018) Overview of the application of geospatial technology to groundwater potential mapping in Nigeria. Arab J GeoSci 11(17):504. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12517-018-3852-4
Akinlalu AA, Adegbuyiro A, Adiat KAN, Akeredolu BE, Lateef WY (2017) Application of multi-criteria decision analysis in prediction of groundwater resources potential: a case of Oke-Ana, Ilesa Area Southwestern, Nigeria. Nriag J Astron Geophys 6(1):184–200. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.nrjag.2017.03.001
Al-Adamat RAN, Foster IDL, Baban SMJ (2003) Groundwater vulnerability and risk mapping for the Basaltic aquifer of the Azraq basin of Jordan using GIS, Remote sensing and DRASTIC. Appl Geogr 23(4):303–324. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.apgeog.2003.08.007
Al-Djazouli MO, Elmorabiti K, Rahimi A, Amellah O, Fadil OAM (2021) Delineating of groundwater potential zones based on remote sensing GIS and analytical hierarchical process: a case of Waddai eastern Chad. GeoJournal 86(4):1881–1894. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10708-020-10160-0
Al-Fugara A, Ahmadlou M, Al-Shabeeb AR, AlAyyash S, Al-Amoush H, Al-Adamat R (2022) Spatial mapping of groundwater springs potentiality using grid search-based and genetic algorithm-based support vector regression. GeoCarto Int 37(1):284–303. https://doi.org/10.1080/10106049.2020.1716396
Andrade R, Guru B (2020) Recharge site delineation through integrated geophysical hydrological and GIS approach – a basic understanding with case studies from Indian sub-continent. Groundw Sustain Dev 10:100–343. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.gsd.2020.100343
Arulbalaji P, Padmalal D, Sreelash K (2019) GIS and AHP techniques based delineation of groundwater potential zones: a case study from Southern Western Ghats, India. Sci Rep 9(1):2082. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41598-019-38567-x
Aykut T (2021) Determination of groundwater potential zones using geographical information systems (GIS) and analytic hierarchy process (AHP) between Edirne-Kalkansogut (northwestern Turkey). Groundw Sustain Dev 12:100545
Banerjee P, Ghose MK, Pradhan R (2018) AHP-based spatial analysis of water quality impact assessment due to change in vehicular traffic caused by highway broadening in Sikkim Himalaya. Appl Water Sci 8(2):72. https://doi.org/10.1007/s13201-018-0699-5
Barua S, Mukhopadhyay BP, Bera A (2021) Integrated assessment of groundwater potential zone under agricultural dominated areas in the western part of Dakshin Dinajpur district, West Bengal, India. Arab J GeoSci 14(11):1042. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12517-021-07312-y
Bera A, Mukhopadhyay BP, Barua S (2020) Delineation of groundwater potential zones in Karha river basin, Maharashtra, India, using AHP and geospatial techniques. Arab J GeoSci 13(15):693. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12517-020-05702-2
Beven KJ, Kirkby MJ (1979) A physically based, variable contributing area model of basin hydrology / Un modèle à base physique de zone d’appel variable de l’hydrologie du bassin versant. Hydrolog Sci J 24(1):43–69. https://doi.org/10.1080/02626667909491834
Chakrabortty R, Pal SC, Malik S, Das B (2018) Modeling and mapping of groundwater potentiality zones using AHP and GIS technique: a case study of Raniganj Block, Paschim Bardhaman, West Bengal. Model Earth Syst Environ 4(3):1085–1110. https://doi.org/10.1007/s40808-018-0471-8
Chang DY (1996) Applications of the extent analysis method on fuzzy AHP. Eur J Oper Res 95(3):649–655. https://doi.org/10.1016/0377-2217(95)00300-2
Chen Y, Chen W, Chandra Pal S, Saha A, Chowdhuri I, Adeli B, Mosavi A (2022) Evaluation efficiency of hybrid deep learning algorithms with neural network decision tree and boosting methods for predicting groundwater potential. GeoCarto Int 37(19):5564–5584
Chenini I, Mammou AB, El May M (2010) Groundwater Recharge Zone Mapping Using GIS-Based Multi-criteria Analysis: A Case Study in Central Tunisia (Maknassy Basin). Water Resour Manag 24(5):921–939. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11269-009-9479-1
Conforti M, Aucelli PPC, Robustelli G, Scarciglia F (2011) Geomorphology and GIS analysis for mapping gully erosion susceptibility in the Turbolo stream catchment (Northern Calabria, Italy). Nat Hazards 56(3):881–898. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11069-010-9598-2
Das B, Pal SC (2020a) Assessment of groundwater vulnerability to over-exploitation using MCDA, AHP, fuzzy logic and novel ensemble models: a case study of Goghat-I and II blocks of West Bengal, India. Environ Earth Sci 79(5):104. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12665-020-8843-6
Das B, Pal SC (2020b) Assessment of groundwater recharge and its potential zone identification in groundwater-stressed Goghat-I block of Hugli District, West Bengal, India. Environ Dev Sustain 22(6):5905–5923. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10668-019-00457-7
Das S, Pardeshi SD (2018) Integration of different influencing factors in GIS to delineate groundwater potential areas using IF and FR techniques: a study of Pravara basin, Maharashtra. India Appl Water Sci 8(7):197. https://doi.org/10.1007/s13201-018-0848-x
Das S, Pardeshi SD, Kulkarni PP, Doke A (2018) Extraction of lineaments from different azimuth angles using geospatial techniques: a case study of Pravara basin, Maharashtra. India Arab J Geosci 11(8):160. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12517-018-3522-6
Das N, Sutradhar S, Ghosh R, Mondal P, Islam S (2021) The response of groundwater to multiple concerning drivers and its future: a study on Birbhum District, West Bengal, India. Appl Water Sci 11(4):1–22
Diaz-Alcaide S, Martínez-Santos P (2019) Advances in groundwater potential mapping. Hydrogeol J 27(7):2307–2324
Doke AB, Zolekar RB, Patel H, Das S (2021) Geospatial mapping of groundwater potential zones using multi-criteria decision-making AHP approach in a hardrock basaltic terrain in India. Ecol Indic 127:107685
Edet AE, Okereke CS (1997) Assessment of hydrogeological conditions in basement aquifers of the Precambrian Oban massif, southeastern Nigeria. J Appl Geophys 36(4):195–204. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0926-9851(96)00049-3
Etikala B, Golla V, Li P, Renati S (2019) Deciphering groundwater potential zones using MIF technique and GIS: a study from Tirupati area, Chittoor District, Andhra Pradesh, India. HydroResearch 1:1–7
Ghosh M, Gope D (2021) Hydro-morphometric characterization and prioritization of sub-watersheds for land and water resource management using fuzzy analytical hierarchical process (FAHP): a case study of upper Rihand watershed of Chhattisgarh State. India Appl Water Sci 11(2):17. https://doi.org/10.1007/s13201-020-01340-x
Gopinath G, Nair AG, Ambili GK, Swetha TV (2016) Watershed prioritization based on morphometric analysis coupled with multi criteria decision making. Arab J Geosci 9(2):129. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12517-015-2238-0
Gouasmia M, Mhamdi A, Dhahri F, Moumni L, Soussi M (2022) Geophysical and hydrogeological investigation to study the aquifer potential of northern Gafsa basin (central Tunisia). Arab J Geosci 15(5):1–10
Halder S, Roy MB, Roy PK (2020) Fuzzy logic algorithm based analytic hierarchy process for delineation of groundwater potential zones in complex topography. Arab J Geosci 13(13):1–22. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12517-020-05525-1
Han WJ, Tsay WD (1998) Formulation of quality strategy using analytic hierarchy process. Twenty-seven annual meeting of the western decision science institute. University of Northern Colorado, USA, pp 580–583
Heleika MA, Toney S, Ismail E (2021) Mapping of groundwater opportunities for multi-purposes use in Beni-Suef province, Egypt. Arab J Geosci 14(9):784. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12517-021-07123-1
Horton RE (1945) Erosional development of streams and their drainage basins; hydrophysical approach to quantitative morphology. Geol Soc Am Bull 56(3):275–370
Jaiswal RK, Mukherjee S, Krishnamurthy J, Saxena R (2003) Role of remote sensing and GIS techniques for generation of groundwater prospect zones towards rural development—an approach. Int J Remote Sens 24(5):993–1008. https://doi.org/10.1080/01431160210144543
Jasrotia AS, Kumar A, Singh R (2016) Integrated remote sensing and GIS approach for delineation of groundwater potential zones using aquifer parameters in Devak and Rui watershed of Jammu and Kashmir, India. Arab J Geosci 9(4):304. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12517-016-2326-9
Jha MK, Chowdhury A, Chowdary VM, Peiffer S (2007) Groundwater management and development by integrated remote sensing and geographic information systems: prospects and constraints. Water Resour Manag 21(2):427–467. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11269-006-9024-4
Jhariya DC, Kumar T, Gobinath M, Diwan P, Kishore N (2016) Assessment of groundwater potential zone using remote sensing, GIS and multi criteria decision analysis techniques. J Geol Soc India 88(4):481–492. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12594-016-0511-9
Khorchani H, Kamel S (2020) Contribution of the resistivity method to the determination of the fault zone and the hydro-geophysical characteristics of the aquifer system in Tataouine (Southern Tunisia). J Afr Earth Sci 172:103942
Kim GB, Hwang CI, Choi MR (2021) Assessment of the need and potential for groundwater artificial recharge based on the water supply water demand and aquifer properties in a water shortage region of South Korea. Environ Earth Sci 3:115. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12665-021-09445-5
Kumar T, Gautam AK, Kumar T (2014) Appraising the accuracy of GIS-based multi-criteria decision-making technique for delineation of Groundwater potential zones. Water Resour Manag 28(13):4449–4466. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11269-014-0663-6
Lee S, Hyun Y, Lee MJ (2019a) Groundwater potential mapping using data mining models of big data analysis in Goyang-si, South Korea. Sustainability 11(6):1678. https://doi.org/10.3390/su11061678
Lee S, Lee CW, Kim JC (2019b) Groundwater productivity potential mapping using logistic regression and boosted tree models: the case of Okcheon City in Korea. Advances in Remote Sensing and Geo Informatics Applications. Springer, Cham, pp 305–307
Machiwal D, Jha MK, Mal BC (2011) Assessment of groundwater potential in a semi-arid region of India using remote sensing, GIS and MCDM techniques. Water Resour Manag 25(5):1359–1386. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11269-010-9749-y
Maity B, Mallick SK, Das P, Rudra S (2022) Comparative analysis of groundwater potentiality zone using fuzzy AHP frequency ratio and Bayesian weights of evidence methods. Appl Water Sci 12(4):63. https://doi.org/10.1007/s13201-022-01591-w
Mallick J, Khan RA, Ahmed M, Alqadhi SD, Alsubih M, Falqi I, Hasan MA (2019) Modeling groundwater potential zone in a semi-arid region of Aseer using fuzzy-AHP and geoinformation techniques. Water 11(12):2656
Masetti M, Poli S, Sterlacchini S (2007) The use of the weights-of-evidence modeling technique to estimate the vulnerability of groundwater to nitrate contamination. Nat Resour Res 16(2):109–119. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11053-007-9045-6
Messerschmid C, Lange J, Sauter M (2018) Field-based groundwater recharge and leakage estimations in a semi-arid Eastern Mediterranean karst catchment, Wadi Natuf, West Bank. Hydrol Earth Syst Sci Discuss 1–38. https://doi.org/10.5194/hess-2018-329
Mogaji KA, Lim HS, Abdullah K (2015) Regional prediction of groundwater potential mapping in a multifaceted geology terrain using GIS-based Dempster-Shafer model. Arab J GeoSci 8(5):3235–3258. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12517-014-1391-1
Moustafa M (2017) Groundwater flow dynamic investigation without drilling boreholes. Appl Water Sci 7(1):481–488. https://doi.org/10.1007/s13201-015-0267-1
Mukherjee P, Singh CK, Mukherjee S (2012) Delineation of groundwater potential zones in arid region of India—a remote sensing and GIS approach. Water Resour Manag 26(9):2643–2672. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11269-012-0038-9
Murmu P, Kumar M, Lal D, Sonker I, Singh SK (2019) Delineation of groundwater potential zones using geospatial techniques and analytical hierarchy process in Dumka district, Jharkhand, India. Groundw Sustain Dev 9:100239. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.gsd.2019.100239
Nguyen PT, Ha DH, Jaafari A, Nguyen HD, Van Phong T, Al-Ansari N, Pham BT (2020) Groundwater potential mapping combining artificial neural network and real AdaBoost ensemble technique: the DakNong province case-study, Vietnam. Int J Env Res Pub He 17(7):2473
Nithya CN, Srinivas Y, Magesh NS, Kaliraj S (2019) Assessment of groundwater potential zones in Chittar basin, Southern India using GIS based AHP technique. Remote Sens Appl: Soc Environ 15:100248
NITI Aayog - Annual Report (2017–2018) Government of India. https://www.niti.gov.in/writereaddata/files/document.../Annual-Report-English.pdf. Accessed 16 Dec 2020
Omeje ET, Ugbor DO, Ibuot JC, Obiora DN (2021) Assessment of groundwater repositories in Edem, Southeastern Nigeria, using vertical electrical sounding. Arab J GeoSci 14(6):421. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12517-021-06769-1
Pal SC, Ghosh C, Chowdhuri I (2020) Assessment of groundwater potentiality using geospatial techniques in Purba Bardhaman district, West Bengal. Appl Water Sci 10(10):22datta1. https://doi.org/10.1007/s13201-020-01302-3
Pradhan AMS, Kim YT, Shrestha S, Huynh TC, Nguyen BP (2021) Application of deep neural network to capture groundwater potential zone in mountainous terrain, Nepal Himalaya. Environ Sci Pollut Res 28(15):18501–18517
Prakash K, Rawat D, Singh S, Chaubey K, Kanhaiya S, Mohanty T (2019) Morphometric analysis using SRTM and GIS in synergy with depiction: a case study of the Karmanasa River basin, North central India. Appl Water Sci 9(1):13. https://doi.org/10.1007/s13201-018-0887-3
Rahman MA, Rusteberg B, Uddin MS, Lutz A, Saada MA, Sauter M (2013) An integrated study of spatial multicriteria analysis and mathematical modelling for managed aquifer recharge site suitability mapping and site ranking at Northern Gaza coastal aquifer. J Environ Manage 124:25–39. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jenvman.2013.03.023
Rahmati O, Pourghasemi HR, Melesse AM (2016) Application of GIS-based data driven random forest and maximum entropy models for groundwater potential mapping: a case study at Mehran Region, Iran. CATENA 137:360–372. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.catena.2015.10
Rane NL, Jayaraj GK (2022) Comparison of multi-influence factor, weight of evidence and frequency ratio techniques to evaluate groundwater potential zones of basaltic aquifer systems. Environ Dev Sustain 24(2):2315–2344
Rehman HU, Ahmad Z, Ashraf A, Ali SS (2019) Predicting groundwater potential zones in Upper Thal Doab, Indus Basin through integrated use of RS and GIS techniques and groundwater flow modeling. Arab J GeoSci 12(19):621. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12517-019-4783-4
Roy DK, Datta B (2019) An ensemble meta-modelling approach using the Dempster-Shafer theory of evidence for developing saltwater intrusion management strategies in coastal aquifers. Water Resour Manag 33:775–795. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11269-018-2142-y
Roy S, Sahu AS (2016) Effectiveness of basin morphometry, remote sensing, and applied geosciences on groundwater recharge potential mapping: A comparative study within a small watershed. Front Earth Sci-Pre 10(2):274–291. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11707-016-0558-3
Roy S, Bose A, Mandal G (2022) Modeling and mapping geospatial distribution of groundwater potential zones in Darjeeling Himalayan region of India using analytical hierarchy process and GIS technique. Model Earth Syst Environ 8(2):1563–1584. https://doi.org/10.1007/s40808-021-01174-9
Roy S, Sahu AS (2015) Investigation for potential groundwater recharge area over the Kunur river basin, Eastern India: an integrated approach with geosciences. J Geomat 9(2):165–177. https://www.researchgate.net/publication/281855321
Saaty TL (1990) How to make a decision: the analytic hierarchy process. Eur J Oper Res 48:9–26. https://doi.org/10.1016/0377-2217(90)90057-I
Saha D, Dhar YR, Vittala SS (2010) Delineation of groundwater development potential zones in parts of marginal Ganga Alluvial Plain in South Bihar, Eastern India. Environ Monit Assess 165(1–4):179–191. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10661-009-0937-2
Sander P (2007) Lineaments in groundwater exploration: A review of applications and limitations. Hydrogeol J 15(1):71–74. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10040-006-0138-9
Saraf AK, Choudhury PR (1998) Integrated remote sensing and GIS for groundwater exploration and identification of artificial recharge sites. Int J Remote Sens 19(10):1825–1841. https://doi.org/10.1080/014311698215018
Saranya T, Saravanan S (2020) Groundwater potential zone mapping using analytical hierarchy process (AHP) and GIS for Kancheepuram District, Tamilnadu, India. Model Earth Syst Environ 6(2):1105–1122
Saravanan S, Saranya T, Jennifer JJ, Singh L, Selvaraj A, Abijith D (2020) Delineation of groundwater potential zone using analytical hierarchy process and GIS for Gundihalla watershed, Karnataka, India. Arab J GeoSci 13(15):695. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12517-020-05712-0
Selvam S, Magesh NS, Chidambaram S, Rajamanickam M, Sashikkumar MC (2015) A GIS based identification of groundwater recharge potential zones using RS and IF technique: a case study in Ottapidaram taluk, Tuticorin district, Tamil Nadu. Environ Earth Sci 73(7):3785–3799. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12665-014-3664-0
Senapati U, Das TK (2021) Assessment of basin-scale groundwater potentiality mapping in drought-prone upper Dwarakeshwar River basin, West Bengal, India, using GIS-based AHP techniques. Arab J Geosci 14(11):960. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12517-021-07316-8
Singha S, Das P, Singha SS (2021) A fuzzy geospatial approach for delineation of groundwater potential zones in Raipur district, India. Groundw Sustain Dev 12:100529
Solomon S, Quiel F (2006) Groundwater study using remote sensing and geographic information systems (GIS) in the central highlands of Eritrea. Hydrogeol J 14(5):729–741. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10040-005-0477-y
Srdjevic B, Medeiros YDP (2008) Fuzzy AHP assessment of water management plans. Water Resour Manag 22(7):877–894. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11269-007-9197-5
Srivastava PK, Bhattacharya AK (2006) Groundwater assessment through an integrated approach using remote sensing, GIS and resistivity techniques: a case study from a hard rock terrain. Int J Remote Sens 27(20):4599–4620. https://doi.org/10.1080/01431160600554983
Taha AI, Al Deep M, Mohamed A (2021) Investigation of groundwater occurrence using gravity and electrical resistivity methods: a case study from Wadi Sar, Hijaz Mountains, Saudi Arabia. Arab J Geosci 14(5):334. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12517-021-06628-z
Tamiru H, Wagari M (2022) Comparison of ANN model and GIS tools for delineation of groundwater potential zones Fincha Catchment, Abay Basin, Ethiopia. Geocarto Int 37(23):6736–6754. https://doi.org/10.1080/10106049.2021.1946171
Thapa R, Gupta S, Gupta A, Reddy DV, Kaur H (2018) Use of geospatial technology for delineating groundwater potential zones with an emphasis on water-table analysis in Dwarka River basin, Birbhum, India. Hydrogeol J 26(3):899–922. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10040-017-1683-0
Touzani M, Mohsine I, Ouardi J, Kacimi I, Morarech M, El Bahajji MH, El Mahrad B (2021) Mapping the pollution plume using the self-potential geophysical method: case of Oum Azza Landfill, Rabat, Morocco. Water 13(7):961
Xu H, Wang D, Ding Z, Deng Z, Shi Y, Yu D, Ye X (2020) Application of convolutional neural network in predicting groundwater potential using remote sensing: a case study in southeastern Liaoning, China. Arab J Geosci 13(15):1–12
Yariyan P, Avand M, Omidvar E, Pham QB, Linh NTT, Tiefenbacher JP (2022) Optimization of statistical and machine learning hybrid models for groundwater potential mapping. Geocarto Int 37(13):3877–3911. https://doi.org/10.1080/10106049.2020.1870164
Yıldırım U (2021) Identification of groundwater potential zones using GIS and multi-criteria decision-making techniques: a case study upper Coruh River basin (NE Turkey). Isprs Int J Geo-Inf 10(6):396
Zandi J, Ghazvinei PT, Hashim R, Yusof KBW, Ariffin J, Motamedi S (2016) Mapping of regional potential groundwater springs using logistic regression statistical method. Water Resour 43(1):48–57. https://doi.org/10.1134/S0097807816010097
Acknowledgements
The authors thank the editor-in-chief for acceptance of the paper. We are also greatly thankful to the DST-PURSE II programme, University of Kalyani, Kalyani, Nadia- 741235 for also some financial assistance in the processing of the research paper. The authors would like to thank to the Survey of India (SOI), Central Groundwater Board (CGWB), and National Bureau of Soil Survey and Land Use Planning (NBSSLUP) Government of India, for providing essential data and maps.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
I the undersigned solemnly declare that this work is totally an original contribution has been done by the authors. The entire work or its part has not been submitted to any other Institution for any other degree/diploma/certificate in this university or any other University of India or abroad. Whenever materials (data, theoretical analysis, and text) from other sources have been used, credit has been given to them in the text of the report and their details in the references.
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no competing interests.
Additional information
Responsible Editor: Biswajeet Pradhan
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Ghosh, M., Sahu, A.S. Delineation of groundwater potential zones using AHP and GIS techniques: a case study in Barakar river basin, India. Arab J Geosci 16, 157 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12517-023-11253-z
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12517-023-11253-z