Contents
Toggle
Averse vs. adverse
What’s the difference between averse vs. adverse? These adjectives are frequently confused, and it’s easy to see why: they’re a single letter apart and have similar meanings too.
Still, they are not the same, and should be treated correctly in writing. Allow this post to be a guide on the differences and proper usages of adverse and averse, (to avoid the common confusion).
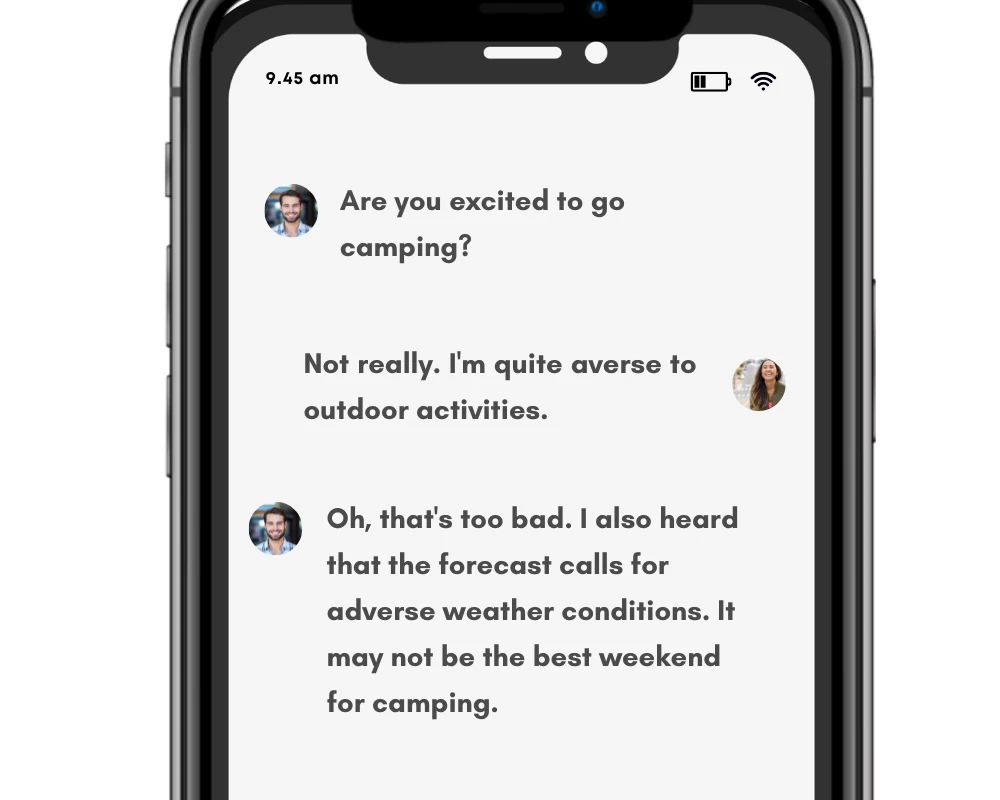
Are “averse” and “adverse” interchangeable?
| Examples with “adverse” | Examples with “averse” |
| The decision to quit her job had an adverse impact on her financial stability. | She was averse to taking risks and preferred her well-established routine. |
Adverse and averse are both adjectives that generally describe feelings of opposition, though they are not interchangeable:
- Averse describes “having an active feeling of repugnance, dislike, or distaste—usually used with to: He seems averse to strenuous exercise“.
- Adverse describes “acting against or in a contrary direction: They were hindered by adverse winds“. Also, something that’s contrary to one’s interests can be adverse: an adverse verdict.
When to use adverse vs. averse
Broadly speaking, when to use averse and adverse concerns what they’re describing. When we use averse, typically it’s in regards to a feeling or a negative emotional response to something. The noun form of averse is aversion, which likewise has to do with personal feelings, or negative feelings towards or about something.
Adverse applies more to actions, effects, conditions or events. Its associated noun forms are adversity and adversary. When you want to describe a negative or deleterious effect that something’s had, (e.g., a certain medication or climate change), the appropriate word in these contexts is adverse.
“Adverse”, used in sentences
| Examples: “adverse’ used in sentences |
| The company’s profits suffered due to the adverse economic conditions in the region. The medication had some adverse side effects, including nausea and dizziness. The team faced adverse weather conditions during their expedition, making the climb even more challenging. Her decision to quit her stable job had an adverse impact on her financial stability. The project was delayed due to a series of adverse events, such as equipment failures and unexpected setbacks. |
“Averse”, used in sentences
| Examples: “averse’ used in sentences |
| She was averse to taking risks and preferred to stick to her well-established routine. Despite his love for adventure, he was averse to the idea of bungee jumping from a high platform. The manager was averse to implementing the new software because he believed it would disrupt the team’s workflow. The child was averse to eating vegetables and would always find ways to avoid them at mealtime. She was averse to public speaking and would get extremely anxious before presentations. |
Synonyms of adverse
- conflicting
- detrimental
- disadvantageous
- inimical
- injurious
- negative
- unfortunate
- unfriendly
- contrary
- opposed
- inopportune
- unpropitious
Synonyms of averse
- reluctant
- disinclined
- hesitant
- hostile
- disliking
- antagonistic
- allergic
- loath
- contrary
- ill-disposed
Origin of adverse
Late 14c., “contrary, opposing,” from Old French advers, earlier avers (13c., Modern French adverse) “antagonistic, unfriendly, contrary, foreign”… from Latin adversus “turned against, turned toward, fronting, facing”.
Origin of averse
Mid-15c., “turned away in mind or feeling, disliking, unwilling,” from Old French avers “hostile, antagonistic” and directly from Latin aversus “turned away, turned back”.
Check out other commonly confused words
Sources
- Harper, Douglas. “Etymology of adverse.” Online Etymology Dictionary, https://www.etymonline.com/word/adverse. Accessed 18 August, 2023.
- Harper, Douglas. “Etymology of averse.” Online Etymology Dictionary, https://www.etymonline.com/word/averse. Accessed 18 August, 2023.
- “Averse.” Merriam-Webster.com Dictionary, Merriam-Webster. Accessed 18 Aug. 2023.
- “Adverse.” Merriam-Webster.com Dictionary, Merriam-Webster. Accessed 18 Aug. 2023.










