How to grow tobacco at home
List of contents
The cultivation and use of tobacco have been practices rooted in different cultures around the world for centuries. From its discovery in the Americas by indigenous natives to its global spread, tobacco has played a fundamental role in the history, economy, industry, and culture of many nations and regions across the globe.
Despite the controversies surrounding tobacco and its consumption, its cultivation continues to be an important activity in various countries, generating employment and contributing to the local economy. Of course, the tobacco plant plays a crucial role in this industry, being instrumental in the production of cigarettes, cigars, pipe stings, and tobacco products such as chewing tobacco. In this article we will explore the different aspects of growing this plant and how you should do it to be successful.

What is tobacco?
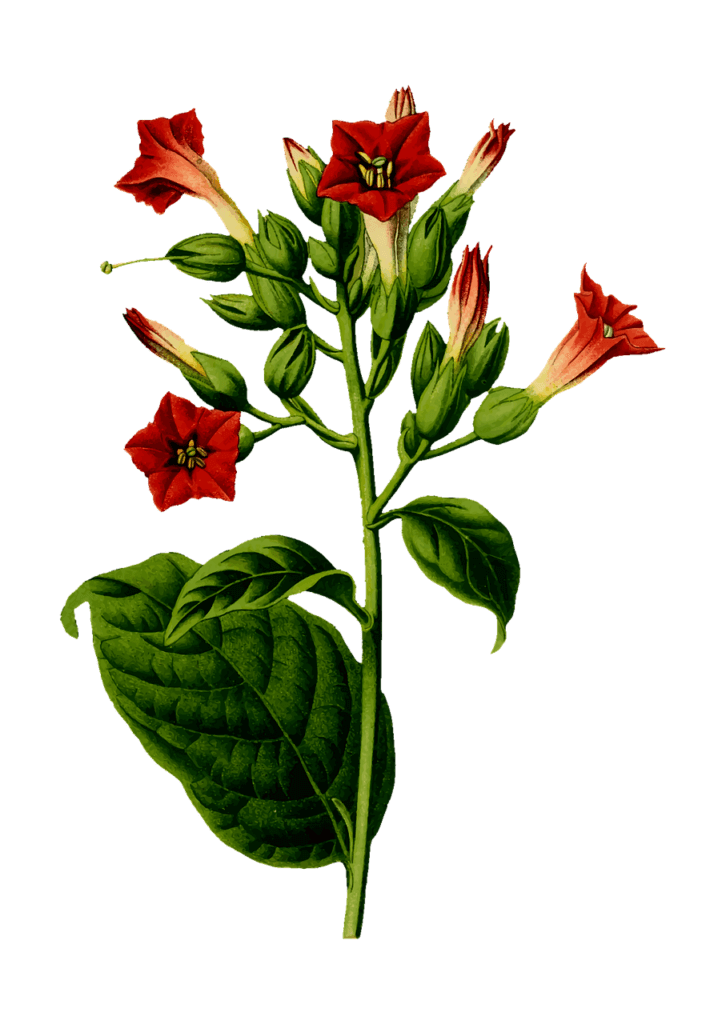
The tobacco plant, scientifically known as Nicotiana tabacum, is a plant belonging to the Solanaceae family. It is native to America, specifically the Andean region, and has been cultivated and used by various cultures for centuries. Like other crops such as potatoes, tomatoes, or corn, tobacco originates from America, which is why it was unknown in Europe until the 16th century when it became a trend despite opposition from organizations such as the Inquisition, known for its unsisterly policies and - even less so - subtle methods.
The plant itself is a herbaceous perennial that grows in the form of a basal rosette during its initial stage and then develops a main stem that can reach a height of up to two meters. Its leaves are large, oval in shape, and have a smooth, waxy surface. Regarding its root system, the tobacco plant has a well-developed taproot and lateral root system that spreads widely into the soil. This allows it to absorb the nutrients necessary for its growth and development.
The leaves of the tobacco plant are, of course, the most valued and used part. They contain several components, the most popular of which is undoubtedly nicotine, an alkaloid that acts as a powerful stimulant and is primarily responsible for the addiction associated with tobacco use, as well as being an excellent insecticide. Apart from nicotine, tobacco leaves contain a wide range of chemical compounds such as alkaloids, sugars, volatile oils, and flavonoids.
What is the difference between blond and black tobacco?
The difference between black and blond tobacco lies mainly in the process of curing and treating the leaves of the plant once harvested, which affects its flavor, aroma, and color. Below we detail the distinctive characteristics of each type of tobacco:
- Black tobacco: Black tobacco, also known as dark tobacco, is characterized by having leaves that have gone through a long curing and fermentation process. During this process, the leaves are exposed to high levels of humidity and controlled heat, which results in a higher concentration of sugars and chemical compounds such as alkaloids and natural oils. These fermented leaves usually take on a dark color, which can vary from brown to black, and have a more intense and complex flavor. Dark tobacco is commonly used in the manufacture of cigars, pipe tobacco, and chewing tobacco.
- Blond tobacco: Blond tobacco, also known as light or gold tobacco, is characterized by having leaves that have gone through a shorter curing process and without prolonged fermentation. Blond tobacco leaves are quickly dried after harvest to preserve their light color and maintain a smoother, more delicate flavor. This type of tobacco is usually used in the manufacture of cigarettes, where a lighter and smoother flavor is sought.
In addition to differences in flavor and color, dark and blond tobacco may also have slightly different nutrient profiles and nicotine content due to variations in the curing and fermentation processes.
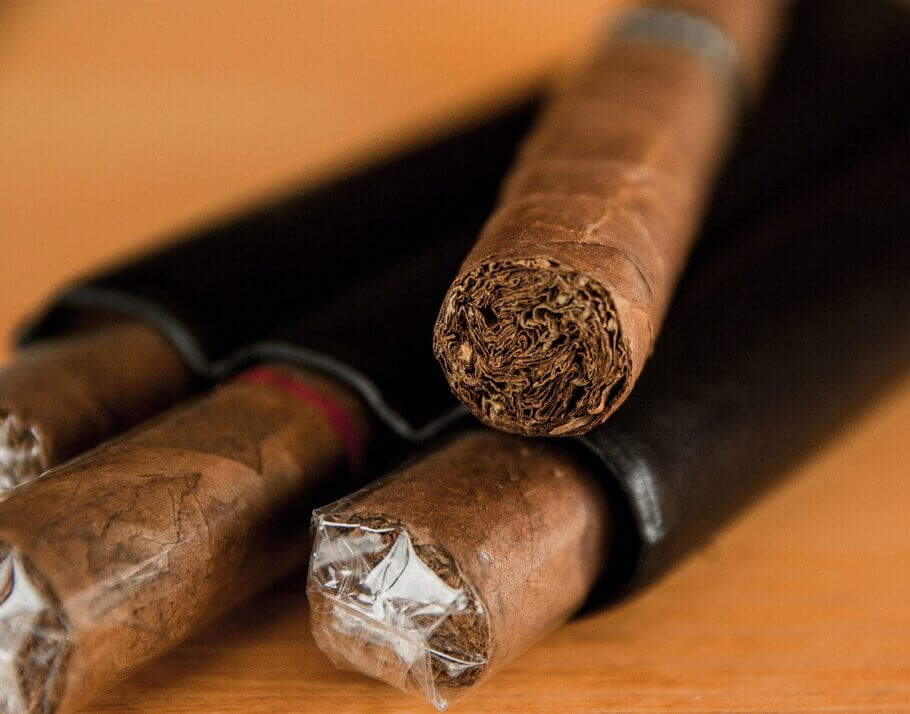

Characteristics of tobacco cultivation
The tobacco plant requires specific climatic conditions for optimal growth, preferring warm climates and well-drained soils. Although it is a resistant and adaptable plant, its cultivation requires proper care and agricultural techniques to obtain a quality product.
The tobacco growing process includes several stages, from sowing the seeds in seedbeds to harvesting the mature leaves. As we know, these leaves are subsequently dried and fermented to improve their flavor and aroma before being used in the production of cigarettes, cigars, and other related products. Here are some of the main aspects of its cultivation:
Ideal climatic and soil conditions for tobacco
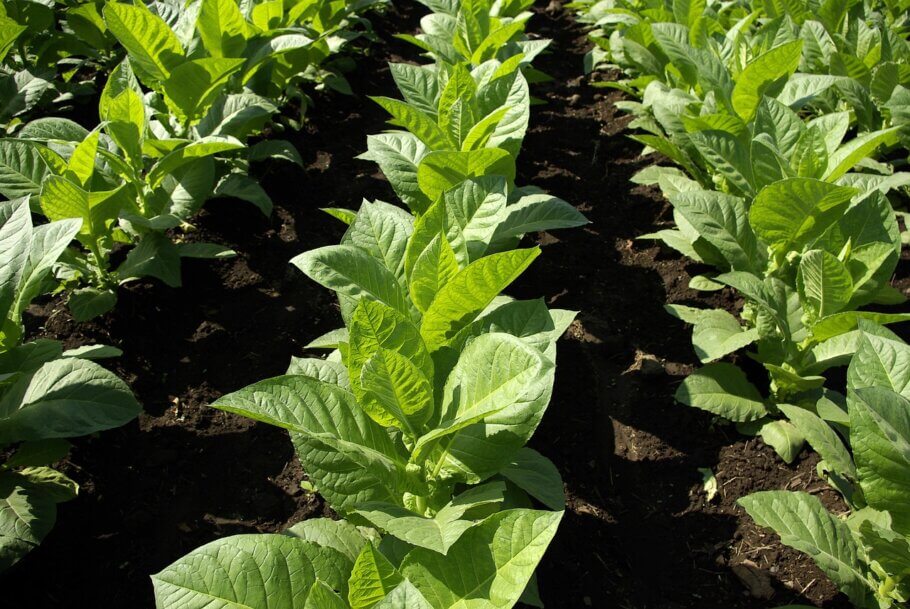
The tobacco plant does not like extreme climates, preferring warm weather conditions and well-drained soil for optimal growth. Below we detail the climatic and soil conditions that favor its cultivation and with which you will obtain the best results:
- Climate: Tobacco requires a warm climate for its proper development. Prefers average temperatures between 20°C and 30°C during the growing season. Frost can seriously damage plants, so it is grown mainly in frost-free regions. However, some varieties of tobacco can tolerate slightly lower temperatures for short periods, such as Delgold tobacco or Costa Rica 589 tobacco.
- Light: The tobacco plant needs significant exposure to sunlight to grow healthily. A minimum of 6 to 8 hours of direct sunlight per day is recommended. Adequate sunlight promotes photosynthesis and contributes to the development of large and healthy leaves, which will result in a better-quality final product.

- Irrigation and rainfall: Tobacco prefers regions with adequate rainfall and well distributed throughout the year. An optimal range of precipitation for tobacco cultivation is between 800 and 1,500 millimeters per year. However, it is important to avoid prolonged periods of heavy rain or waterlogging, as this can negatively affect plant development and increase the risk of fungal diseases and hence the use of fungicides.
- Soil: Ideally, well-drained and fertile soils, loamy or sandy-loamy, and rich in organic matter. The ideal soil pH for tobacco generally ranges from 5.5 to 6.5, slightly acidic to neutral. In addition, good soil drainage is essential to avoid waterlogging, since excess moisture can favor the development of diseases.
It is important to note that the exact conditions may vary depending on the variety of tobacco grown and the geographic region. Tobacco farmers often tailor growing practices to the specific conditions in their area for the best results.

Tobacco Plant Nutrition
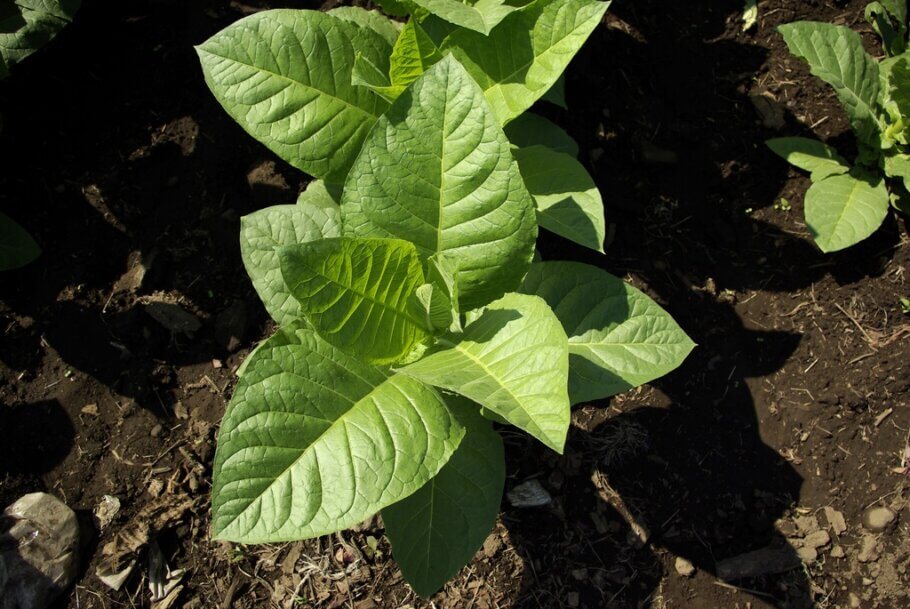
The tobacco plant requires a variety of nutrients for its healthy growth and development. These nutrients are divided into macronutrients and micronutrients, and each one plays a crucial role in the metabolism and production of the plant. Here are the essential nutrients needed for your tobacco plants to grow happily and smoothly:
Macronutrients:
- Nitrogen (N): Nitrogen is essential for plant growth and the formation of proteins and chlorophyll. It is especially important in the early stages of plant development and in the production of healthy green leaves.
- Phosphorus (P): Phosphorus plays a critical role in energy transfer and in the development of strong roots and healthy root systems. It is also essential for the proper maturation of flowers and the formation of seeds.
- Potassium (K): Potassium contributes to plant resistance to stress, improves tobacco quality, and helps regulate water. It also plays an important role in photosynthesis and protein synthesis.
Micronutrients:
- Iron (Fe): Iron is essential for the formation of chlorophyll and therefore for photosynthesis. It is also necessary for protein synthesis and other metabolic processes.
- Manganese (Mn): Manganese is important for enzyme activity and photosynthesis. It helps in the production of energy and in the formation of chlorophyll.
- Zinc (Zn): Zinc is involved in protein synthesis and in the development of new cells. It is also necessary for the formation of chlorophyll and root growth.
These are just a few examples of the essential nutrients for growing tobacco, although in addition to these, the plant also requires other elements such as calcium, magnesium, sulfur, copper, molybdenum, and boron in adequate amounts. It is important for tobacco farmers to maintain a proper balance of nutrients in the soil through the application of fertilizers and proper management practices, which will ensure healthy plant growth and quality tobacco production.

Phases of tobacco cultivation
The life cycle of a tobacco plant can vary slightly depending on the variety grown, climatic conditions, and specific management practices. However, in general, it can be divided into the following stages:
- Seed germination: This stage marks the beginning of the plant's life cycle. Tobacco seeds are sown in seedbeds or germination trays, where adequate humidity and temperature conditions are provided. Germination usually occurs within 7 to 10 days after sowing.
- Young Seedlings: After germination, the seedlings emerge from the soil and develop their first true leaves. During this stage, the seedlings require special care, such as regular watering and protection against diseases and pests. The duration of this stage is usually 4 to 6 weeks.
- Vegetative growth: Once the seedlings reach an adequate size and the climatic conditions are favorable, the transplant to the field is carried out. The seedlings are placed in rows in the prepared soil, where they will continue their growth and development. At this stage, the tobacco plant develops additional leaves and increases in size, so providing adequate irrigation and nutrients is essential to promote healthy growth. The duration of this stage can be approximately 6 to 10 weeks.
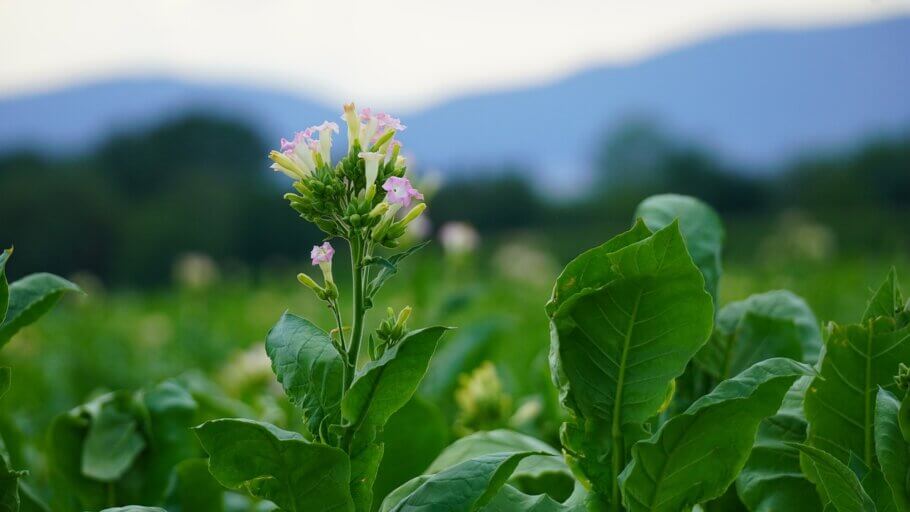

- Flowering and seed production: After vegetative growth, the tobacco plant enters the flowering stage, where it will produce a floral cluster at the top, forming flowers that give rise to the development of capsules that contain the seeds. The length of this stage can vary but generally lasts 6 to 8 weeks.
- Leaf Ripening: Once the tobacco plant has completed the flowering and seed production stage, the tobacco leaves begin to ripen. During this phase, the leaves acquire their color and specific characteristics according to the cultivated variety. The maturation of the leaves can take from 4 to 8 weeks.
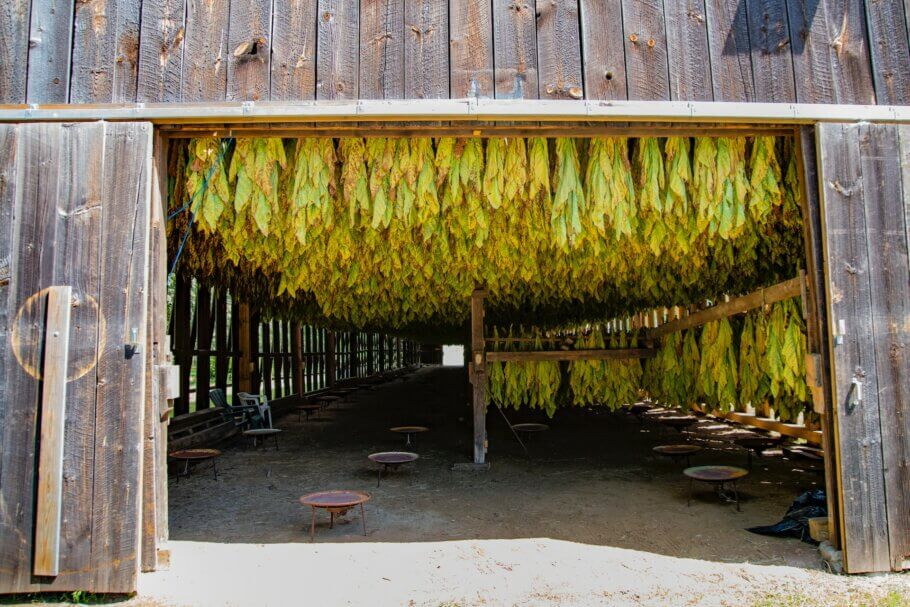
- Harvest: The last stage of the life cycle is the harvest of the mature leaves. The upper leaves of the plant are collected, usually in several rounds, as they reach proper maturity. The duration and frequency of harvesting depend on the type of tobacco and the harvesting practices used.

How to grow tobacco plants step by step
If you have a few tobacco seeds and you want to grow them, you just have to follow this guide to do it without complications:
- The best way to germinate your little seeds is to use seedbeds until the plant is ready to be transplanted, which can take several weeks from germination. Leave them somewhere with good lighting but no direct light, even indoors, and try to spray the seedbed with water daily (so that it never dries up!). If you have few plants, you can use a plant propagator to increase humidity. A good time to start is spring (although professional growers usually start a bit earlier, even in winter).
- Once your little plants are 10-15cm, which can take 3-4 weeks, you can transplant them into a larger pot. If you are going to grow the plants in a pot, make sure that it is at least 11 liters and, if possible, white. On the other hand, if you plan to finish the cultivation in mother soil, choose a slightly smaller pot to grow it for another 3-4 weeks before the final transplant outdoors.
- After this time, about 6 weeks from when you germinated the seeds or when your plants measure 15-20cm, it is time to place them in their final place. Choose a site with many hours of daily sun and transplant your plants into the ground, or place your pots in that area (shading the pots in some way will help the root temperature not rise excessively in summer). In case you observe yellowing of the leaves at any time, try to use a fertilizer rich in nitrogen. It is important that the plants do not dry out, so you may need to water them daily for the first few days in full sun.
- Once you see signs in your plants that flowering is beginning, they will produce a flower cluster at the apical tip of the stem; remove this flower. After a few days, new shoots or shoots may form where the leaves meet the stem; remove them too or the quality of your tobacco will decrease. Try to keep the substrate free of weeds and undergrowth throughout the crop. As harvest time approaches, the lower leaves of the plant may deteriorate, don't worry.
- About 3 months after you planted, or about 3-4 weeks after removing the flower cluster, it is time to start the harvest. Congratulations!! You have managed to grow your tobacco plants successfully and now all that remains is to dry them correctly for later use, something that we will teach you how to do in a future article.
Until then!