Abstract
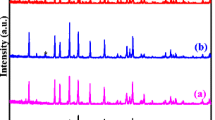
Lithium-ion batteries (LIBs) based on solid-state electrolytes have attracted much attention for their high safety and energy density. Li29Zr9Nb3O40 (LZNO), as a new kind of Li-ion conductor, has great potential in applications of solid-state LIBs. In this work, various contents of LiF are selected to modify LZNO Li-ion conductor, and the optimal content of LiF is 5 wt% (weight%). The phase component, crystal structure, ionic conductivity, and electrochemical performance are investigated. The refinement of crystallographic information based on the bond valence site energy theory is induced to reveal the possible lithium-ion migration channel. The results show that modification with LiF enhanced the 3D migration pathways and conductivity of LZNO-based electrolytes. The 5 wt% LiF modified LZNO presents total conductivity of 0.943 × 10−4 S cm−1 at ambient temperature and has low activation energy of conduction (0.16 eV). The cycle performance of the lithium symmetric cell characterizes the cycle of 140 h.








Similar content being viewed by others
Data availability
The datasets generated during and/or analyzed during the current study are available from the corresponding author on reasonable request.
References
L. Li, Y. Deng, G. Chen, Status and prospect of garnet/polymer solid composite electrolytes for all-solid-state lithium batteries. J. Energy Chem. 50, 154–177 (2020)
J. Ma, Y. Li, N.S. Grundish, J.B. Goodenough, Y. Chen, L. Guo, Z. Peng, X. Qi, F. Yang, L. Qie, C.-A. Wang, B. Huang, Z. Huang, L. Chen, D. Su, G. Wang, X. Peng, Z. Chen, J. Yang, S. He, X. Zhang, H. Yu, C. Fu, M. Jiang, W. Deng, C.-F. Sun, Q. Pan, Y. Tang, X. Li, X. Ji, F. Wan, Z. Niu, F. Lian, C. Wang, G.G. Wallace, M. Fan, Q. Meng, S. Xin, Y.-G. Guo, L.-J. Wan, The 2021 battery technology roadmap. J. Phys. D: Appl. Phys. 54, 183001 (2021)
G.V. Alexander, I.M. S, R. Murugan, Review on the critical issues for the realization of all-solid-state lithium metal batteries with garnet electrolyte: interfacial chemistry, dendrite growth, and critical current densities. Ionics 27, 4105–4126 (2021)
F. Wu, J. Maier, Y. Yu, Guidelines and trends for next-generation rechargeable lithium and lithium-ion batteries. Chem. Soc. Rev. 49, 1569–1614 (2020)
L. Xu, J. Li, H. Shuai, Z. Luo, B. Wang, S. Fang, G. Zou, H. Hou, H. Peng, X. Ji, Recent advances of composite electrolytes for solid-state Li batteries. J. Energy Chem. 67, 524–548 (2022)
J.C. Bachman, S. Muy, A. Grimaud, H.H. Chang, N. Pour, S.F. Lux, O. Paschos, F. Maglia, S. Lupart, P. Lamp, L. Giordano, Y. Shao-Horn, Inorganic solid-state electrolytes for lithium batteries: mechanisms and properties governing ion conduction. Chem. Rev. 116, 140–162 (2016)
N. Kamaya, K. Homma, Y. Yamakawa, M. Hirayama, R. Kanno, M. Yonemura, T. Kamiyama, Y. Kato, S. Hama, K. Kawamoto, A. Mitsui, A lithium superionic conductor. Nat. Mater. 10, 682–686 (2011)
B. Tao, C. Ren, H. Li, B. Liu, X. Jia, X. Dong, S. Zhang, H. Chang, Thio-/LISICON and LGPS-type solid electrolytes for all-solid-state lithium-ion batteries. Adv. Funct. Mater. 32, 2203551 (2022)
S. Kundu, A. Kraytsberg, Y. Ein-Eli, Recent development in the field of ceramics solid-state electrolytes: I-oxide ceramic solid-state electrolytes. J. Solid State Electrochem. (2022). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10008-022-05206-x
X. Lu, F. Zhang, J. Li, The influence of lithium sources on properties of perovskite-type lithium ion conductor. J. Alloys Compd. 875, 159887 (2021)
X. Song, T. Zhang, T.D. Christopher, Y. Guo, S. Huang, Y. Liu, T. Söhnel, P. Cao, Achieving enhanced densification and superior ionic conductivity of garnet electrolytes via a co-doping strategy coupled with pressureless sintering. J. Eur. Ceram. Soc 42, 5023–5028 (2022)
H. Huo, X. Li, Y. Sun, X. Lin, K. Doyle-Davis, J. Liang, X. Gao, R. Li, H. Huang, X. Guo, X. Sun, Li2CO3 effects: new insights into polymer/garnet electrolytes for dendrite-free solid lithium batteries. Nano Energy 73, 104836 (2020)
P. Lightfoot, J.B. Thomson, F.J. Little, P.G. Bruce, Ab initio determination of crystal structures by X-ray powder diffraction: structure of Li29Zr9Nb3O40. J. Mater. Chem. 4, 167–169 (1994)
J. Shao, Z. Li, Y. Zeng, S. Chen, L. Yang, H. Zhang, Li29Zr9Nb3O40 based Li-ionic conductors as a new system of solid-state electrolytes. J. Alloys Compd. 816, 152517 (2020)
J. Chen, H. Zhang, L. Yang, H. Chen, J. Shao, Z. Li, High Li-ionic conductivity of Li29Zr9Nb3O40 ceramic sintered in oxygen-deficient atmosphere. J. Alloys Compd. 896, 163082 (2022)
G.G. Amatucci, N. Pereira, Fluoride based electrode materials for advanced energy storage devices. J. Fluor. Chem 128, 243–262 (2007)
J. Ko, Y.S. Yoon, Recent progress in LiF materials for safe lithium metal anode of rechargeable batteries: is LiF the key to commercializing Li metal batteries? Ceram. Int 45, 30–49 (2019)
Y. Liu, R. Tao, S. Chen, K. Wu, Z. Zhong, J. Tu, P. Guo, H. Liu, S. Tang, J. Liang, Y.-C. Cao, A novel polyurethane-LiF artificial interface protective membrane as a promising solution towards high-performance lithium metal batteries. J. Power Sources 477, 228694 (2020)
J. Ko, Y.S. Yoon, Lithium fluoride layer formed by thermal evaporation for stable lithium metal anode in rechargeable batteries. Thin Solid Films 673, 119–125 (2019)
K. Lee, S. Han, J. Lee, S. Lee, J. Kim, Y. Ko, S. Kim, K. Yoon, J.-H. Song, J.H. Noh, K. Kang, Multifunctional interface for high-rate and long-durable garnet-type solid electrolyte in lithium metal batteries. ACS Energy Lett. 7, 381–389 (2021)
Y. Ruan, Y. Lu, Y. Li, C. Zheng, J. Su, J. Jin, T. Xiu, Z. Song, M.E. Badding, Z. Wen, A 3D cross-linking lithiophilic and electronically insulating interfacial engineering for garnet‐type solid‐state lithium batteries. Adv. Funct. Mater. 31, 2007815 (2020)
L. Xiong, Z. Ren, Y. Xu, S. Mao, P. Lei, M. Sun, LiF assisted synthesis of LiTi2(PO4)3 solid electrolyte with enhanced ionic conductivity. Solid State Ionics 309, 22–26 (2017)
Z. Yao, K. Zhu, J. Zhang, J. Li, X. Li, J. Wang, K. Yan, J. Liu, LiF-assisted synthesis of perovskite-type Li0.35La0.55TiO3 solid electrolyte for rechargeable lithium-metal batteries. J. Electron. Mater. 51, 736–744 (2021)
T. Lei, L. Xue, Y. Li, Y. Chen, J. Zhu, S. Deng, X. Lian, G. Cao, W. Li, Enhanced electrochemical performances via introducing LiF electrolyte additive for lithium ion batteries. Ceram. Int. 45, 18106–18110 (2019)
Y. Lu, X. Meng, J.A. Alonso, M.T. Fernandez-Diaz, C. Sun, Effects of fluorine doping on structural and electrochemical properties of Li6.25Ga0.25La3Zr2O12 as electrolytes for solid-state lithium batteries. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 11, 2042–2049 (2019)
R.U.I. Kun, W.E.N. Zhao-Yin, L.I.U. Cai, High ion conductivity in garnet-type F-doped Li7La3Zr2O12. J. Inorg. Mater. 30, 995–1001 (2015)
X. Ma, Y. Xu, Efficient anion fluoride-doping strategy to enhance the performance in garnet-type solid electrolyte Li7La3Zr2O12. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 14, 2939–2948 (2022)
S.R. Yeandel, B.J. Chapman, P.R. Slater, P. Goddard, Structure and lithium-ion dynamics in fluoride-doped cubic Li7La3Zr2O12 (LLZO) garnet for Li solid-state battery applications. J. Phys. Chem. C 122, 27811–27819 (2018)
L. Yang, Z. Li, C. Gao, S. Gong, J. Chen, H. Chen, H. Zhang, Li2ZrO3 based Li-ion conductors doped with halide ions & sintered in oxygen-deficient atmosphere. Ceram. Int. 47, 31907–31914 (2021)
B.H. Toby, R.B. Von Dreele, GSAS-II: the genesis of a modern open-source all purpose crystallography software package. J. Appl. Crystallogr. 46, 544–549 (2013)
L.L. Wong, K.C. Phuah, R. Dai, H. Chen, W.S. Chew, S. Adams, Bond valence pathway analyzer—an automatic rapid screening tool for fast ion conductors within softBV. Chem. Mater 33, 625–641 (2021)
K. Momma, F. Izumi, VESTA 3 for three-dimensional visualization of crystal, volumetric and morphology data. J. Appl. Crystallogr. 44, 1272–1276 (2011)
J. Wang, Z. Zhang, H. Ying, G. Han, W.-Q. Han, In-situ formation of LiF-rich composite interlayer for dendrite-free all-solid-state lithium batteries. Chem. Eng. J. 411, 128534 (2021)
Funding
This work is supported by the research funds from the National Natural Science Foundation of China (No. 51767021) and Development Funds of Hunan Wedid Materials Technology Co., Ltd., China (No. 738010241).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
ZL, HZ, and HC contributed to the study conception and design. Material preparation, data collection, and analysis were performed by HC, JC, EX, and YW. The first draft of the manuscript was written by HC, and all authors commented on previous versions of the manuscript. All authors read and approved the final manuscript.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Competing interests
The authors have no relevant financial or non-financial interests to disclose.
Additional information
Publisher’s Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Supplementary Information
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Chen, H., Li, Z., Chen, J. et al. Crystallographic structure and electrical properties of LiF modified Li29Zr9Nb3O40 for electrolyte of solid-state batteries. J Mater Sci: Mater Electron 33, 26775–26787 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10854-022-09343-x
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10854-022-09343-x