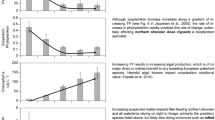
Abstract
We studied the effects of varying levels of nitrogen (N), phosphorus (P), and nitrogen and phosphorus mixture (NP) enrichment on the hatching of resting eggs to determine whether nutrient enrichment levels affect the emergence of zooplankton from resting eggs. We treated resting eggs with six different nutrient concentrations and returned them to the in situ water environment to simulate the restoration of a favourable environment after eutrophication. Low nutrient concentrations had a lesser impact on egg hatching compared with high concentrations, and P had a lesser impact on egg hatching than N and NP. Resting eggs were able to maintain their vitality even in unfavourable environments during the enrichment phase, and they hatched in large numbers when favourable conditions arose. High concentrations of N and NP had a significant effect on the community structure of hatched zooplankton, mainly affecting the emergence of copepod nauplii from resting eggs. The findings suggest that levels of nutrient enrichment determine the emergence of zooplankton from resting egg banks. This study provides a reference for the potential replenishment of active populations by resting egg banks in eutrophic river environments.





Similar content being viewed by others
Data availability
The datasets generated during and/or analysed during the current study are available from the corresponding author on reasonable request.
References
Abrusán, G., P. Fink & W. Lampert, 2007. Biochemical limitation of resting egg production inDaphnia. Limnology and Oceanography 52: 1724–1728. https://doi.org/10.4319/lo.2007.52.4.1724.
Aranguiz-Acuna, A. & P. Perez-Portilla, 2017. Metal stress in zooplankton diapause production: post-hatching response. Ecotoxicology 26: 329–339. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10646-017-1766-7.
Ban, S., 1992. Effects of photoperiod, temperature, and population density on induction of diapause egg production in Eurytemora Affinis (Copepoda: Calanoida) in Lake Ohnuma, Hokkaido, Japan. Journal of Crustacean Biology 12: 361–367. https://doi.org/10.2307/1549029.
Baumgartner, M. F. & A. M. Tarrant, 2017. The physiology and ecology of diapause in marine copepods. Annual Review of Marine Science 9: 387–411. https://doi.org/10.1146/annurev-marine-010816-060505.
Belmonte, G. & A. C. Pati, 2007. Hatching rate and diapause duration in eggs of Paracartia latisetosa (Copepoda: Calanoida). Journal of Plankton Research 29: i39–i47. https://doi.org/10.1093/plankt/fbl064.
Benjamini, Y. & Y. Hochberg, 1995. Controlling the False discovery rate: a practical and powerful approach to multiple testing. Journal of the Royal Statistical Society Series B (methodological) 57: 289–300. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.2517-6161.1995.tb02031.x.
Brede, N., C. Sandrock, D. Straile, P. Spaak, T. Jankowski, B. Streit & K. Schwenk, 2009. The impact of human-made ecological changes on the genetic architecture of Daphnia species. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences 106: 4758–4763. https://doi.org/10.1073/pnas.0807187106.
Brendonck, L. & L. De Meester, 2003. Egg banks in freshwater zooplankton: evolutionary andecological archives in the sediment. Hydrobiologia 491: 65–84. https://doi.org/10.1023/a:1024454905119.
Chen, F. & N. H. J. M. B. Marcus, 1997. Subitaneous, diapause, and delayed-hatching eggs of planktonic copepods from the northern Gulf of Mexico: morphology and hatching success. Marine Biology 127: 587–597. https://doi.org/10.1007/s002270050049.
Chen, L., C. Li, K. Zhou, Y. Shi & M. Liu, 2018. Effects of nutrient limitations on three species of zooplankton. Acta Oceanologica Sinica 37: 58–68. https://doi.org/10.1007/s13131-017-1122-z.
Chittapun, S., P. Pholpunthin & H. Segers, 2005. Restoration of Tropical peat swamp rotifer communities after perturbation: an experimental study of recovery of rotifers from the resting egg bank. Hydrobiologia 546: 281–289. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10750-005-4209-z.
Choi, K.-H., M.-C. Jang, H. H. Shin, W.-J. Lee & K. Shin, 2014. In situ hatching success of Calanoid copepod eggs in hypoxic sediments of a coastal bay. Journal of Coastal Research 32: 333–338. https://doi.org/10.2112/jcoastres-d-14-00096.1.
Clarke, K. R., 1993. Non-parametric multivariate analyses of changes in community structure. Austral Ecology 18: 117–143. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1442-9993.1993.tb00438.x.
Coelho, P. N., T. A. S. V. Paes, P. M. Maia-Barbosa & M. J. dos Santos-Wisniewski, 2021. Effects of pollution on dormant-stage banks of cladocerans and rotifers in a large tropical reservoir. Environmental Science and Pollution Research 28: 30887–30897. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-021-12751-x.
Costa, B. N. S., S. C. C. Pinheiro, M. de Oliveira Lima & L. L. Amado, 2016. Microzooplankton as an indicator of environmental quality at an industrial complex in the Brazilian Amazon. Ecological Indicators 66: 220–229. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ecolind.2016.01.033.
Dahms, H.-U., 1995. Dormancy in the Copepoda-an overview. Hydrobiologia 306: 199–211. https://doi.org/10.1007/bf00017691.
Dong, Y., X. Zheng, Y. Ma, Q. Li, B. Xu & X. Jiang, 2020. Diversity and community structure of zooplankton resting eggs in intertidal mudflats and creeks of an estuary. Journal of Experimental Marine Biology and Ecology 532: 151446. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jembe.2020.151446.
Freiry, R. F., V. Weber, C. C. Bonecker, F. A. Lansac-Tôha, M. M. Pires, C. Stenert & L. Maltchik, 2020. Additive partitioning of the diversity of the dormant zooplankton communities in intermittent ponds along a forest–grassland transition. Hydrobiologia 847: 1327–1342. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10750-020-04187-0.
Gilbert, J. J., 2017. Resting-egg hatching and early population development in rotifers: a review and a hypothesis for differences between shallow and deep waters. Hydrobiologia 796: 235–243. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10750-016-2867-7.
Glippa, O., L. Denis, S. Lesourd & S. Souissi, 2014. Seasonal fluctuations of the copepod resting egg bank in the middle Seine estuary, France: impact on the nauplii recruitment. Estuarine, Coastal and Shelf Science 142: 60–67. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ecss.2014.03.008.
Glippa, O., S. Souissi, L. Denis & S. Lesourd, 2011. Calanoid copepod resting egg abundance and hatching success in the sediment of the Seine estuary (France). Estuarine Coastal and Shelf Science 92: 255–262. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ecss.2010.12.032.
Guizien, K., C. Dupuy, P. Ory, H. Montanié, H. Hartmann, M. Chatelain & M. Karpytchev, 2014. Microorganism dynamics during a rising tide: disentangling effects of resuspension and mixing with offshore waters above an intertidal mudflat. Journal of Marine Systems 129: 178–188. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jmarsys.2013.05.010.
Hairston, N. G., Jr., 1996. Zooplankton egg banks as biotic reservoirs in changing environments. Limnology and Oceanography 41: 1087–1092. https://doi.org/10.4319/lo.1996.41.5.1087.
Hairston, N. G., W. Lampert, C. E. Cáceres, C. L. Holtmeier, L. J. Weider, U. Gaedke, J. M. Fischer, J. A. Fox & D. M. Post, 1999. Rapid evolution revealed by dormant eggs. Nature 401: 446–446. https://doi.org/10.1038/46731.
Hairston, N. G. & W. E. Walton, 1986. Rapid evolution of a life history trait. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences 83: 4831–4833. https://doi.org/10.1073/pnas.83.13.4831.
Hansen, B. W., P. J. Hansen, T. G. Nielsen & P. M. Jepsen, 2017. Effects of elevated pH on marine copepods in mass cultivation systems: practical implications. Journal of Plankton Research 39: 984–993. https://doi.org/10.1093/plankt/fbx032.
Howarth, R. W., A. Sharpley & D. Walker, 2002. Sources of nutrient pollution to coastal waters in the United States: Implications for achieving coastal water quality goals. Estuaries 25: 656–676. https://doi.org/10.1007/bf02804898.
Huang, J., Y. Zhang, H. Bing, J. Peng, F. Dong, J. Gao & G. B. Arhonditsis, 2021. Characterizing the river water quality in China: recent progress and on-going challenges. Water Research 201: 117309. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.watres.2021.117309.
Huang, Y., X. Xie, L. J. Zhou, X. Ji, B. Gao, G. Z. Xu & A. Li, 2019. Multi-phase distribution and risk assessment of endocrine disrupting chemicals in the surface water of the Shaying River, -Huai River Basin, China. Ecotoxicology and Environmental Safety 173: 45–53. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ecoenv.2019.02.016.
Isanta Navarro, J., C. Kowarik, M. Wessels, D. Straile & D. Martin-Creuzburg, 2019. Resilience to changes in lake trophic state: nutrient allocation into Daphnia resting eggs. Ecology & Evolution 9: 12813–12825. https://doi.org/10.1002/ece3.5759.
Jernberg, S., M. Lehtiniemi & L. Uusitalo, 2017. Evaluating zooplankton indicators using signal detection theory. Ecological Indicators 77: 14–22. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ecolind.2017.01.038.
Jiao, S., W. Chen, J. Wang, N. Du, Q. Li & G. Wei, 2018. Soil microbiomes with distinct assemblies through vertical soil profiles drive the cycling of multiple nutrients in reforested ecosystems. Microbiome 6: 1–13. https://doi.org/10.1186/s40168-018-0526-0.
Jorgensen, T. S., P. M. Jepsen, H. C. B. Petersen, D. S. Friis & B. W. Hansen, 2019. Eggs of the copepod Acartia tonsa Dana require hypoxic conditions to tolerate prolonged embryonic development arrest. BMC Ecology 19: 1. https://doi.org/10.1186/s12898-018-0217-5.
Lembrechts, J. J., H. J. De Boeck, J. Liao, A. Milbau & I. Nijs, 2018. Effects of species evenness can be derived from species richness—ecosystem functioning relationships. Oikos 127: 337–344. https://doi.org/10.1111/oik.04786.
Liang, D., Q. Wang, N. Wei, C. Tang, X. Sun & Y. Yang, 2020. Biological indicators of ecological quality in typical urban river-lake ecosystems: the planktonic rotifer communityand its response to environmental factors. Ecological Indicators 112: 106127. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ecolind.2020.106127.
Lindley, J., C. George, S. Evans & P. Donkin, 1998. Viability of calanoid copepod eggs from intertidal sediments: a comparison of three estuaries. Marine Ecology Progress Series 162: 183–190. https://doi.org/10.3354/meps162183.
Lubzens, E., R. Hamo, I. Blais, S. Jeries, O. Almog-Gabai & Y. G. Assaraf, 2020. Rotifer resting eggs: an alternative for rotifer mass cultures in fish farms—lessons from a comprehensive study on production, storage and hatching of resting eggs. Aquaculture 528: 735505. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.aquaculture.2020.735505.
Lukic, D., C. Vad & Z. Horváth, 2016. Isolation by sugar flotation has no direct effect on the hatching success of zooplankton resting eggs. Journal of Limnology 75: 415–421. https://doi.org/10.4081/jlimnol.2016.1385.
Maia-Barbosa, P. M., E. M. Eskinazi-Sant’Anna, C. F. Valadares & G. C. D. Pessoa, 2003. The resting eggs of zooplankton from a tropical, eutrophic reservoir (Pampulha Reservoir, south-east Brazil). Lakes and Reservoirs: Research and Management 8: 269–275. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1440-1770.2003.00229.x.
Marcus, N. H., 1996. Ecological and evolutionary significance of resting eggs in marine copepods: past, present, and future studies. Hydrobiologia 320: 141–152. https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00016815.
Marcus, N. H., R. Lutz, W. Burnett & P. Cable, 1994. Age, viability, and vertical distribution of zooplankton resting eggs from an anoxic basin: evidence of an egg bank. Limnology and Oceanography 39: 154–158. https://doi.org/10.4319/lo.1994.39.1.0154.
Masero, R. & F. Villate, 2004. Composition, vertical distribution and age of zooplankton benthic eggs in the sediments of two contrasting estuaries of the Bay of Biscay. Hydrobiologia 518: 201–212. https://doi.org/10.1023/b:Hydr.0000025063.22926.67.
Möst, M., A. C. Chiaia-Hernandez, M. P. Frey, J. Hollender & P. Spaak, 2015. A mixture of environmental organic contaminants in lake sediments affects hatching from Daphnia resting eggs. Environmental Toxicology and Chemistry 34: 338–345. https://doi.org/10.1002/etc.2808.
Nielsen, D. L., D. Smith & R. Petrie, 2012. Resting egg banks can facilitate recovery of zooplankton communities after extended exposure to saline conditions. Freshwater Biology 57: 1306–1314. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1365-2427.2012.02782.x.
Odriozola, M., H. E. Zagarese & N. Diovisalvi, 2020. Zooplankton hatching from dormant eggs in a large Pampean shallow lake. Hydrobiologia 847: 2097–2111. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10750-020-04233-x.
Oskina, N., T. Lopatina, O. Anishchenko & E. Zadereev, 2018. High resistance of resting eggs of Cladoceran Moina macrocopa to the effect of heavy metals. Bulletin of Environmental Contamination and Toxicology 102: 335–340. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00128-018-2473-7.
Putman, A., D. Martin-Creuzburg, B. Panis & L. De Meester, 2015. A comparative analysis of the fatty acid composition of sexual and asexual eggs of Daphnia magna and its plasticity as a function of food quality. Journal of Plankton Research 37: 752–763. https://doi.org/10.1093/plankt/fbv043.
Radzikowski, J., 2013. Resistance of dormant stages of planktonic invertebrates to adverse environmental conditions. Journal of Plankton Research 35: 707–723. https://doi.org/10.1093/plankt/fbt032.
Radzikowski, J., K. Krupińska & M. Ślusarczyk, 2017. Different thermal stimuli initiate hatching of Daphnia diapausing eggs originating from lakes and temporary waters. Limnology 19: 81–88. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10201-017-0520-4.
Santangelo, J. M., L. R. Araújo & F. D. A. M. R. L. EstevesMancaBozelli, 2011. Method for hatching resting eggs from tropical zooplankton: effects of drying or exposing to low temperatures before incubation. Acta Limnologica Brasiliensia 23: 42–47. https://doi.org/10.4322/actalb.2011.017.
Smart, G. R., 1978. Investigations of the toxic mechanisms of ammonia to fish–gas exchange in rainbow trout (Salmo gairdneri) exposed to acutely lethal concentrations. Journal of Fish Biology 12: 93–104. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1095-8649.1978.tb04155.x.
Sun, R., Y. Chen, W. Han, W. Dong, Y. Zhang, C. Hu, B. Liu & F. Wang, 2020. Different contribution of species sorting and exogenous species immigration from manure to soil fungal diversity and community assemblage under long-term fertilization. Soil Biology and Biochemistry 151: 108049. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.soilbio.2020.108049.
Vandekerkhove, J., S. Declerck, L. U. C. Brendonck, J. M. Conde-Porcuna, E. Jeppesen & L. D. Meester, 2005. Hatching of cladoceran resting eggs: temperature and photoperiod. Freshwater Biology 50: 96–104. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1365-2427.2004.01312.x.
Vandekerkhove, J., B. Niessen, S. Declerck, E. Jeppesen, J. M. Conde Porcuna, L. Brendonck & L. De Meester, 2004. Hatching rate and hatching success with and without isolation of zooplankton resting stages. Hydrobiologia 526: 235–241. https://doi.org/10.1023/B:HYDR.0000041598.68424.fc.
Vargas, A. L., J. M. Santangelo & R. L. Bozelli, 2019. Recovery from drought: viability and hatching patterns of hydrated and desiccated zooplankton resting eggs. International Review of Hydrobiology 104: 26–33. https://doi.org/10.1002/iroh.201801977.
Vehmaa, A., T. Katajisto & U. Candolin, 2018. Long-term changes in a zooplankton community revealed by the sediment archive. Limnology and Oceanography 63: 2126–2139. https://doi.org/10.1002/lno.10928.
von Martels, J. Z. H., A. R. Bourgonje, M. A. Y. Klaassen, H. A. A. Alkhalifah, M. Sadaghian Sadabad, A. Vich Vila, R. Gacesa, R. Y. Gabriels, R. E. Steinert, B. H. Jansen, M. L. C. Bulthuis, H. M. van Dullemen, M. C. Visschedijk, E. A. M. Festen, R. K. Weersma, P. de Vos, H. van Goor, K. N. Faber, H. J. M. Harmsen & G. Dijkstra, 2020. Riboflavin supplementation in patients with Crohn’s disease [the RISE-UP study]. Journal of Crohn’s & Colitis 14: 595–607. https://doi.org/10.1093/ecco-jcc/jjz208.
Wang, L., X. Han, Y. Zhang, Q. Zhang, X. Wan, T. Liang, H. Song, N. Bolan, S. M. Shaheen, J. R. White & J. Rinklebe, 2023. Impacts of land uses on spatio-temporal variations of seasonal water quality in a regulated river basin, Huai River, China. The Science of the Total Environment 857: 159584. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scitotenv.2022.159584.
Wang, Q., L. L. Luan, L. D. Chen, D. N. Yuan, S. Liu, J. S. Hwang & Y. F. Yang, 2016. Recruitment from an egg bank into the plankton in Baisha Bay, a mariculture base in Southern China. Estuarine Coastal & Shelf Science 181: 312–318. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ecss.2016.08.040.
Warkentin, K. M., 2011. Environmentally cued hatching across taxa: embryos respond to risk and opportunity. Integrative and Comparative Biology 51: 14–25. https://doi.org/10.1093/icb/icr017.
Weider, L. J., W. Lampert, M. Wessels, J. K. Colbourne & P. Limburg, 1997. Long–term genetic shifts in a microcrustacean egg bank associated with anthropogenic changes in the Lake Constance ecosystem. Proceedings of the Royal Society of London Series B 264: 1613–1618. https://doi.org/10.1098/rspb.1997.0225.
Wen, X., P. Zhai, R. Feng, R. Yang & Y. Xi, 2017. Comparative analysis of the spatio-temporal dynamics of rotifer community structure based on taxonomic indices and functional groups in two subtropical lakes. Scientific Reports 7: 578. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41598-017-00666-y.
Wyngaard, G. A., 1988. Geographical variation in dormancy in a copepod: evidence from population crosses. Hydrobiologia 167: 367–374. https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00026327.
Zhang, K., D. Deng, W. Wang, S. Peng, F. Liu & L. Ji, 2020. Long-term eutrophication affects vertical changes of Daphnia ephippia in the sediments of a subtropical Chinese lake. Environmental Science and Pollution Research 27: 4737–4745. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-019-07157-9.
Zhang, K., F. Jiang, H. Chen, D. T. Dibar, Q. Wu & Z. Zhou, 2019. Temporal and spatial variations in zooplankton communities in relation to environmental factors in four floodplain lakes located in the middle reach of the Yangtze River, China. Environmental Pollution 251: 277–284. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.envpol.2019.04.139.
Zhang, W., D. P. Swaney, B. Hong, R. W. Howarth, X. J. E. S. Li & P. Research, 2017. Influence of rapid rural-urban population migration on riverine nitrogen pollution: perspective from ammonia-nitrogen. Environmental Science & Pollution Research 24: 27201–27214. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-017-0322-6.
Zhao, K., K. Song, Y. Pan, L. Wang, L. Da & Q. Wang, 2017. Metacommunity structure of zooplankton in river networks: roles of environmental and spatial factors. Ecological Indicators 73: 96–104. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ecolind.2016.07.026.
Zhou, Y., Y. Zhang, T. Liang & L. Wang, 2019. Shifting of phytoplankton assemblages in a regulated Chinese river basin after streamflow and water quality changes. Science of the Total Environment 654: 948–959. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scitotenv.2018.10.348.
Acknowledgements
We thank the staff at the laboratory and field for the sampling and analysis. We are very grateful to the editors and anonymous reviewers for their constructive comments on the manuscript.
Funding
This work was financially supported by the Ecological Environment Special Project of Anhui Provincial Key Research and Development Project (202004i07020012).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
All authors contributed to the study conception and design. LL, conceptualization, methodology, software, visualization, and writing-original draft preparation; LG, writing—reviewing and editing and supervision; YQ, data curation; ZZ, JG and XZ, investigation, resources, validation, and formal analysis. All authors read and approved the final manuscript.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Ethical approval
Not applicable.
Informed consent
Informed consent was obtained from all individual participants included in the study.
Additional information
Handling editor: Ülkü Nihan Tavşanoğlu
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Supplementary Information
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Luan, L., Gao, L., Qiu, Y. et al. Levels of nutrient enrichment determine the emergence of zooplankton from resting egg banks. Hydrobiologia 851, 1259–1273 (2024). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10750-023-05387-0
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10750-023-05387-0